We’ve answered many different kinds of questions for many different organisations in over 70 countries. They include:
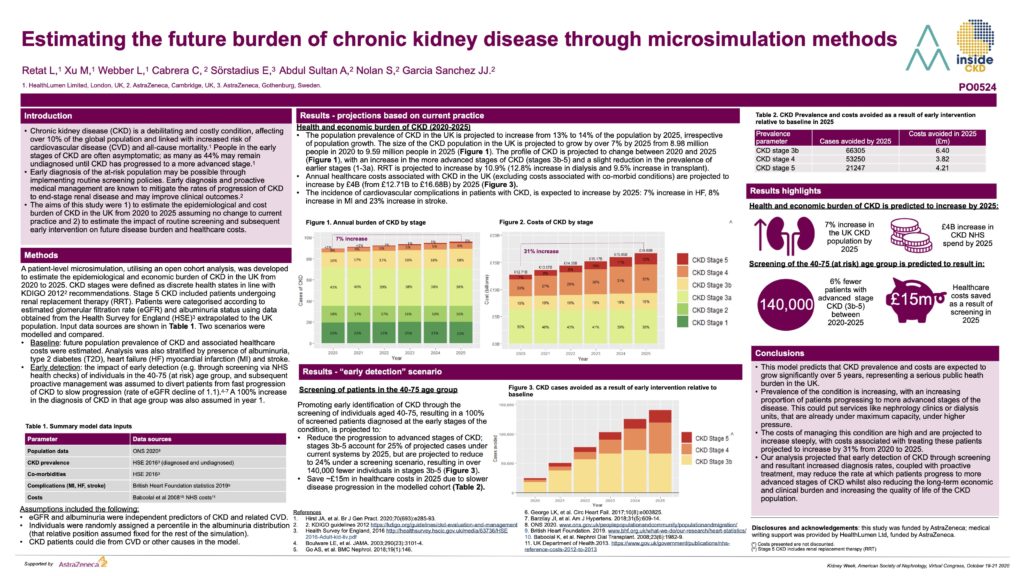
Chronic kidney disease (CKD) is a debilitating and costly condition, affecting over 10% of the global population and linked with increased risk of cardiovascular disease (CVD) and all-cause mortality. People in the early stages of CKD are often asymptomatic; as many as 44% may remain undiagnosed until CKD has progressed to a more advanced stage. Early diagnosis of the at-risk population may be possible through implementing routine screening policies. Early diagnosis and proactive medical management are known to mitigate the rates of progression of CKD to end-stage renal disease and may improve clinical outcomes. The aims of this study were 1) to estimate the epidemiological and cost burden of CKD in the UK from 2020 to 2025 assuming no change to current practice and 2) to estimate the impact of routine screening and subsequent early intervention on future disease burden and healthcare costs. Undertaken in partnership with AstraZeneca, this study is now being rolled out to over 20 countries.

The COVID-19 pandemic has increased interest in Universal Basic Income (UBI) as a means of addressing a range of socio-economic insecurities. While previous trials of cash transfer schemes have often focused on low-level transfers inadequate to satisfy the needs for which the policy was originally developed, emerging pilots are moving toward a position of increasing generosity. Our multidisciplinary project, Examining the Health Case for UBI, has brought together colleagues in behavioural science, public health, epidemiology and economics to establish pathways to health impact.
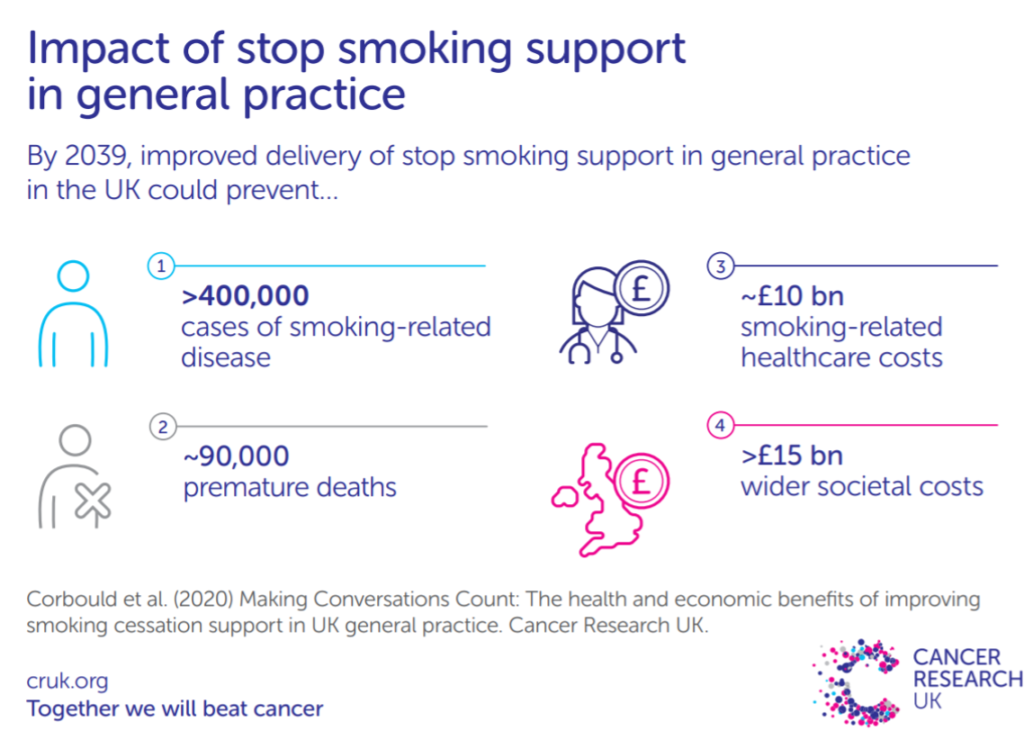
This study conducted with Cancer Research UK aimed to quantify the health and economic benefits of GPs routinely delivering stop smoking support to patients during consultations in the UK. Using a microsimulation model over the period 2019 to 2039, a current practice 'baseline' scenario was compared to three opt-out smoking cessation intervention scenarios.
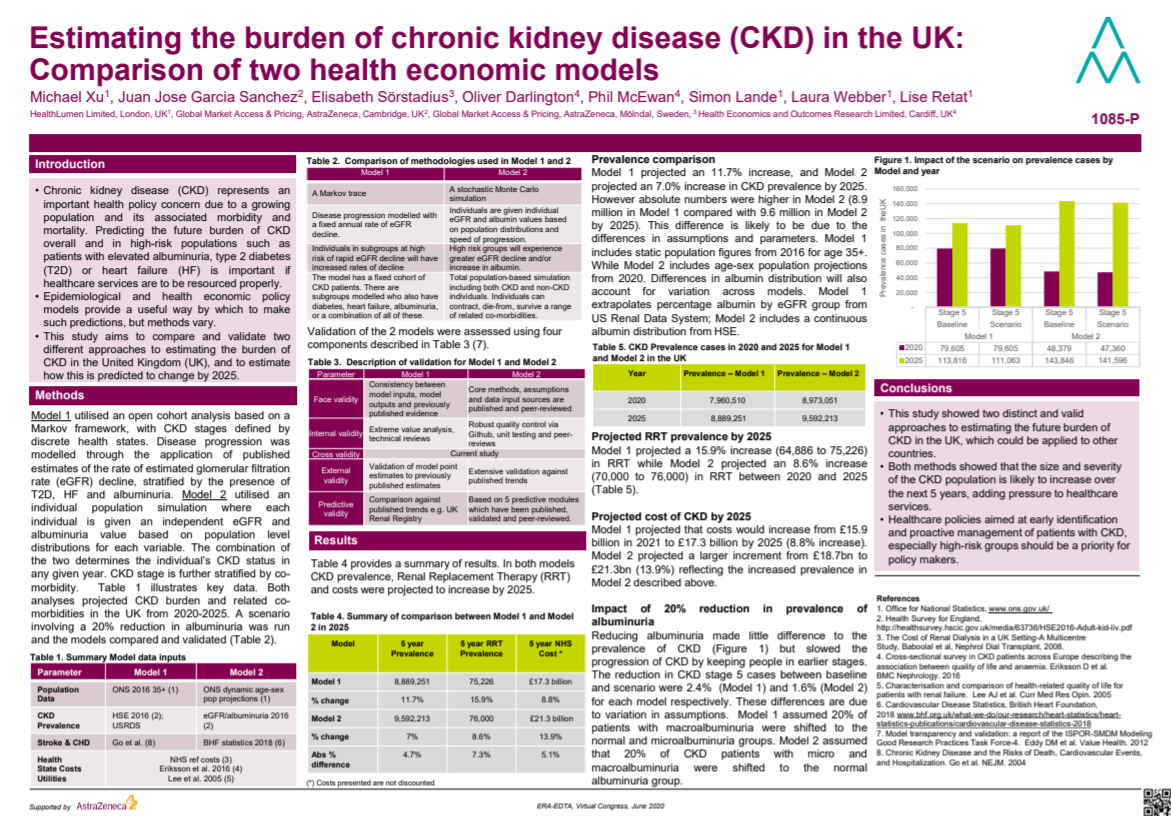
Chronic kidney disease (CKD) represents an important health policy concern due to a growing population and its associated morbidity and mortality. Predicting the future burden of CKD overall and in high-risk populations such as patients with elevated albuminuria, type 2 diabetes (T2D) or heart failure is important if healthcare services are to be resourced properly. Epidemiological and health economic policy models provide a useful way by which to make such predictions, but methods vary. This study aims to compare and validate two different approaches to estimating the burden of CKD in the United Kingdom (UK), and to estimate how this is predicted to change by 2025. Undertaken in partnership with AstraZeneca, this study is now being rolled out to over 20 countries.

The COVID-19 Pandemic is projected to cause an economic shock larger than the Global Financial Crisis of 2007/2008 and a recession as great as anything seen since the Great Depression in 1930s. The social and economic consequences of lockdowns and social distancing measures, such as unemployment, broken relationships and homelessness create potential for inter-generational trauma extending decades into the future. In the absence of a vaccine, governments need to introduce Universal Basic Income (UBI) as a means of mitigating this trauma.

In 2019, we reviewed Universal Basic Income (UBI) trial design and findings in comparison with the social gradient in health literature and biopsychosocial theory to identify knowledge gaps. The findings highlight a need to refocus UBI trials on improved health, including via reduced stress, to provide policy makers the means of producing accurate cost-benefit analysis. Previous trials have either not reflected likely UBI policy or failed to measure impacts that enable accurate analysis.
We have an experienced and multi-disciplinary team of software engineers, population health and policy research experts, and mathematicians.
Team